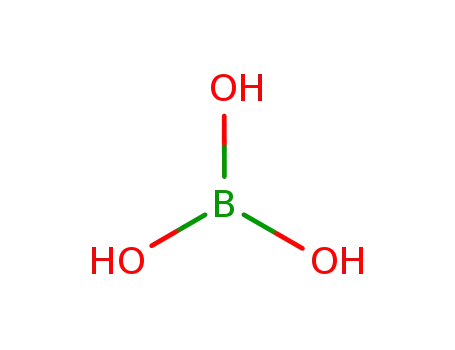
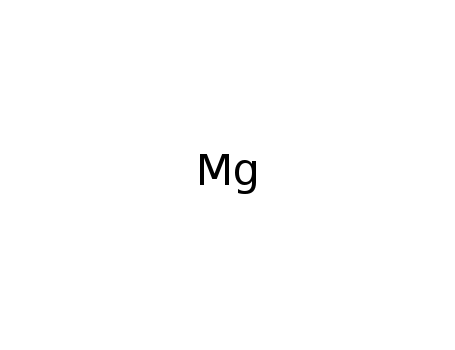Synthesis of plate-like ZrB2 grains
Hu, Chunfeng,Zou, Ji,Huang, Qing,Zhang, Guojun,Guo, Shuqi,Sakka, Yoshio
, p. 85 - 88 (2012)
Plate-like ZrB2 grains were synthesized ...
Surface electronic structure of ZrB2 buffer layers for GaN growth on Si wafers
Yamada-Takamura, Yukiko,Bussolotti, Fabio,Fleurence, Antoine,Bera, Sambhunath,Friedlein, Rainer
, (2010)
The electronic structure of epitaxial, p...
New borothermal reduction route to synthesize submicrometric ZrB 2 powders with low oxygen content
Guo, Wei-Ming,Zhang, Guo-Jun
, p. 3702 - 3705 (2011)
The ZrB2 powders with submicrometric par...
ZrB2 powders synthesis by borothermal reduction
Ran, Songlin,Van Der Biest, Omer,Vleugels, Jef
, p. 1586 - 1590 (2010)
High-purity zirconium diboride (ZrB2) po...
Synthesis of ZrB2 powders by carbothermal and borothermal reduction
Jung, Eun-Young,Kim, Jung-Hun,Jung, Se-Hyuk,Choi, Sung-Churl
, p. 164 - 168 (2012)
Zirconium diboride (ZrB2) powders were s...
Reaction processes and characterization of ZrB2 powder prepared by boro/carbothermal reduction of ZrO2 in vacuum
Guo, Wei-Ming,Zhang, Guo-Jun
, p. 264 - 267 (2009)
The present work was concentrated mainly...
Epitaxial growth of group III nitrides on silicon substrates via a reflective lattice-matched zirconium diboride buffer layer
Tolle,Roucka,Tsong,Ritter,Crozier,Chizmeshya,Kouvetakis
, p. 2398 - 2400 (2003)
The growth of metallic and reflecting Zr...
Reactive hot pressing of ZrB2-SiC-ZrC ultra high-temperature ceramics at 1800°C
Wu, Wen-Wen,Zhang, Guo-Jun,Kan, Yan-Mei,Wang, Pei-Ling
, p. 2967 - 2969 (2006)
A ZrB2-SiC-ZrC composite was prepared fr...
Thermal Properties of Hf-Doped ZrB2 Ceramics
Lonergan, Jason M.,McClane, Devon L.,Fahrenholtz, William G.,Hilmas, Gregory E.
, p. 2689 - 2691 (2015)
The effect of Hf additions on the therma...
Aerospace application on Al 2618 with reinforced – Si3N4, AlN and ZrB2in-situ composites
Mathan Kumar,Senthil Kumaran,Kumaraswamidhas
, p. 238 - 250 (2016)
In this study, the Al 2618 aluminium all...
Morphology evolution of ZrB2 nanoparticles synthesized by solgel method
Zhang, Yun,Li, Ruixing,Jiang, Yanshan,Zhao, Bin,Duan, Huiping,Li, Junping,Feng, Zhihai
, p. 2047 - 2052 (2011)
Zirconium diboride (ZrB2) nanoparticles ...
Mechanosynthesis of Hf1-xZrxB2 solid solution and Hf1-xZrxB2/SiC composite powders
Aviles, Miguel A.,Cordoba, Jose M.,Sayagues, Maria J.,Alcala, Maria D.,Gotor, Francisco J.
, p. 696 - 702 (2010)
The synthesis of solid solutions in the ...
Formation of zirconium diboride (ZrB2) by room temperature mechanochemical reaction between ZrO2, B2O3 and Mg
Setoudeh,Welham
, p. 225 - 228 (2006)
A mixture of magnesium, boric oxide and ...
Effect of carbon and titanium carbide on sintering behaviour of zirconium diboride
Mishra,Pathak
, p. 547 - 555 (2008)
Systematic sintering studies on the ZrB2...
Pressureless densification of zirconium diboride with boron carbide additions
Zhang,Hilmas,Fahrenholtz
, p. 1544 - 1550 (2006)
Zirconium diboride (ZrB2) was densified ...
Epitaxial semimetallic HfxZr1-xB2 templates for optoelectronic integration on silicon
Roucka, Radek,An, YuJin,Chizmeshya, Andrew V. G.,Tolle, John,Kouvetakis, John,D'Costa, Vijay R.,Menendez, Jose,Crozier, Peter
, (2006)
High quality heteroepitaxial Hfx Zr1-x B...
Fabrication of UHTCs by conversion of dynamically consolidated Zr+B and Hf+B powder mixtures
Brochu, Mathieu,Gauntt, Bryan,Zimmerly, Tony,Ayala, Alicia,Loehman, Ronald
, p. 2815 - 2822 (2008)
Mixtures of Zr+B and Hf+B were shock com...
Synthesis of ZrB2 and ZrB2-SiC powders using a sucrose-containing system
Wang, Tingyu,Zhang, Yun,Li, Junping,Zhao, Bin,Li, Ruixing,Yin, Shu,Feng, Zhihai,Sato, Tsugio,Cai, Hongnian
, p. 7402 - 7406 (2015)
ZrB2 and ZrB2-SiC powders are synthesize...
Microstructure and properties of spark plasma-sintered ZrO 2-ZrB2 nanoceramic composites
Basu, Bikramjit,Venkateswaran,Kim, Doh-Yeon
, p. 2405 - 2412 (2006)
In a recent work,1 we have reported the ...
Nanocarbon-dependent synthesis of ZrB2 in a binary ZrO 2 and boron system
Li, Ruixing,Lou, Haijie,Yin, Shu,Zhang, Yun,Jiang, Yanshan,Zhao, Bin,Li, Junping,Feng, Zhihai,Sato, Tsugio
, p. 8581 - 8583 (2011)
Thermodynamically, ZrO2 may react with b...
Synthesis of ZrB2 powders by molten-salt participating silicothermic reduction
Li, Mengrui,Ke, Changming,Zhang, Jinhua
, (2020)
A novel molten-salt silicothermic reduct...
Synthesis and thermal stability of Zr(BH4)4 and Zr(BD4)4 produced by mechanochemical processing
Gennari,Fernández Albanesi,Rios
, p. 3731 - 3737 (2009)
Zirconium tetrahydroborate Zr(BH4)4 and ...
An investigation on the formation mechanism of nano ZrB2 powder by a magnesiothermic reaction
Jalaly,Bafghi, M.Sh.,Tamizifar,Gotor
, p. 36 - 41 (2014)
Nanocrystalline zirconium diboride (ZrB2...
Synthesis and microstructure of zirconium diboride formed from polymeric precursor pyrolysis
Xie, Changming,Chen, Mingwei,Wei, Xi,Ge, Min,Zhang, Weigang
, p. 866 - 869 (2012)
Zirconium diboride was synthesized by py...
ZIRCONIUM BOROHYDRIDE AS A ZIRCONIUM BORIDE PRECURSOR.
Rice,Woodin
, p. c181-c183 (1988)
Synthesis of zirconium boride, ZrB//2, f...
Boron Carbide-Zirconium Boride in Situ Composites by the Reactive Pressureless Sintering of Boron Carbide-Zirconia Mixtures
Goldstein, Adrian,Geffen, Ygal,Goldenberg, Ayala
, p. 642 - 644 (2001)
The heating of B4C-YTZP (where YTZP deno...
Synthesis and characterization of a novel precursor-derived ZrC/ZrB 2 ultra-high-temperature ceramic composite
Wang, Hao,Chen, Xingbo,Gao, Bo,Wang, Jun,Wang, Yingde,Chen, Shugang,Gou, Yanzi
, p. 79 - 84 (2013)
ZrC and ZrB2, two valuable members of ul...
Mechanochemical processing of nanocrystalline zirconium diboride powder
Guo, Shuqi,Hu, Chunfeng,Kagawa, Yutaka
, p. 3643 - 3647 (2011)
Nanocrystalline ZrB2 powder was prepared...
Thermal Expansion of Micro- and Nanocrystalline ZrB2 Powders
Kalinnikov, G. V.,Khomenko, N. Yu.,Konovalikhin, S. V.,Korobov, I. I.,Kovalev, D. Yu.,Kravchenko, S. E.,Shilkin, S. P.
, p. 258 - 264 (2020)
Abstract—: Nano- and microcrystalline Zr...
Low-temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline ZrB2 via co-reduction of ZrCl4 and BBr3
Chen, Luyang,Gu, Yunle,Shi, Liang,Ma, Jianhua,Yang, Zeheng,Qian, Yitai
, p. 1423 - 1424 (2004)
Nanocrystalline zirconium diboride (ZrB2...
Preparation of zirconium boride powder
Zhao,He,Jin
, p. 2534 - 2536 (1995)
An intermediate reaction in the synthesi...
Reaction chemistry during self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) of H3BO3-ZrO2-Mg system
Khanra
, p. 2224 - 2229 (2007)
In the present investigation, the ZrB2 p...
Preparation and microstructure of a ZrB2-SiC composite fabricated by the spark plasma sintering-reactive synthesis (SPS-RS) method
Zhao, Yuan,Wang, Lian-Jun,Zhang, Guo-Jun,Jiang, Wan,Chen, Li-Dong
, p. 4040 - 4042 (2007)
A mixture of Zr, B4C, and Si powders was...
Electronic transport in MgB2, AlB2 and ZrB2 - A comparative study
Fisher,Chashka,Patlagan,Reisner
, p. 1 - 10 (2003)
We report on the temperature dependence ...
Thermal and electrical transport properties of spark plasma-sintered HfB2 and ZrB2 ceramics
Zhang, Luning,Pejakovic, Dusan A.,Marschall, Jochen,Gasch, Matthew
, p. 2562 - 2570 (2011)
The thermal and electrical transport pro...
New route to synthesize ultra-fine zirconium diboride powders using inorganic-organic hybrid precursors
Yan, Yongjie,Huang, Zhengren,Dong, Shaoming,Jiang, Dongliang
, p. 3585 - 3588 (2006)
Ultra-fine zirconium diboride (ZrB2) pow...
The effect of starting precursors on size and shape modification of ZrB2 ceramic nanoparticles
Amirsardari, Zahra,Aghdam, Rouhollah Mehdinavaz,Salavati-Niasari, Masoud,Jahannama, Mohammad Reza
, p. 10017 - 10021 (2015)
The formation of ZrB2 nanoparticles thro...
ZrB2- SiC nano-powder mixture prepared using ZrSi2 and modified spark plasma sintering
Lee, Sea-Hoon,Choi, Si-Young,Kim, Hai-Doo
, p. 1051 - 1054 (2013)
ZrB2-SiC nano-powder mixture was synthes...
Reactive hot pressing of ZrB2-SiC-ZrC composites at 1600°C
Wu, Wen-Wen,Zhang, Guo-Jun,Kan, Yan-Mei,Wang, Pei-Ling
, p. 2501 - 2508 (2008)
A ZrB2-SiC-ZrC ceramic was produced by r...
Improved oxidation resistance of zirconium carbide at 1500°C by lanthanum hexaboride additions
Zhao, Liyou,Jia, Dechang,Duan, Xiaoming,Yang, Zhihua,Zhou, Yu
, p. 3648 - 3650 (2011)
Addition of LaB6 is adopted to improve t...
Nanosized zirconium diboride: Synthesis and properties
Kravchenko,Torbov,Shilkin
, p. 506 - 509 (2011)
The thermolysis of Zr(BH4)4 vapor at 573...
Fully dense ZrB2 ceramics by borothermal reduction with ultra-fine ZrO2 and solid solution
Xu, Liang,Guo, Wei-Ming,Liu, Qiu-Yu,Zhang, Yan,Wu, Li-Xiang,You, Yang,Lin, Hua-Tay
, p. 3133 - 3140 (2022/01/19)
The effects of ZrO2 particle size (55?nm...
Super-hardening and localized plastic deformation behaviors in ZrB2 –TaВ2 ceramics
Klechkovskaya, V. V.,Kurbatkina, V. V.,Levashov, E. A.,Lobova, T. A.,Loginov, P. A.,Patsera, E. I.,Sidnov, K.,Sviridova, T. A.,Vorotilo, S.
, (2022/01/19)
A systematic study of the Zr-Ta-B system...
New criteria for the applicability of combustion synthesis: The investigation of thermodynamic and kinetic processes for binary Chemical Reactions
Tan, Xiaoming,Su, Xianli,Yan, Yonggao,Uher, Ctirad,Zhang, Qingjie,Tang, Xinfeng
supporting information, (2021/01/07)
Combustion synthesis is a novel techniqu...
ZrB2as an earth-abundant metal diboride catalyst for electroreduction of dinitrogen to ammonia
Cheng, Yonghua,Chu, Ke,Guo, Yali,Li, Qingqing,Li, Xiaotian
supporting information, p. 13009 - 13012 (2020/11/07)
ZrB2 is first explored as an earth-abund...